Project Terminal
With the Project Terminal, you gain direct access to your project's command line interface, empowering you to execute commands, manage resources, and streamline workflows effectively. This guide covers the basics of using the terminal, accessing it within your project, and working with different terminal types and pods.
Accessing the Terminal
The terminal provides users with direct access to the command line interface of their projects.
Accessing the terminal in PipeOps is straightforward:
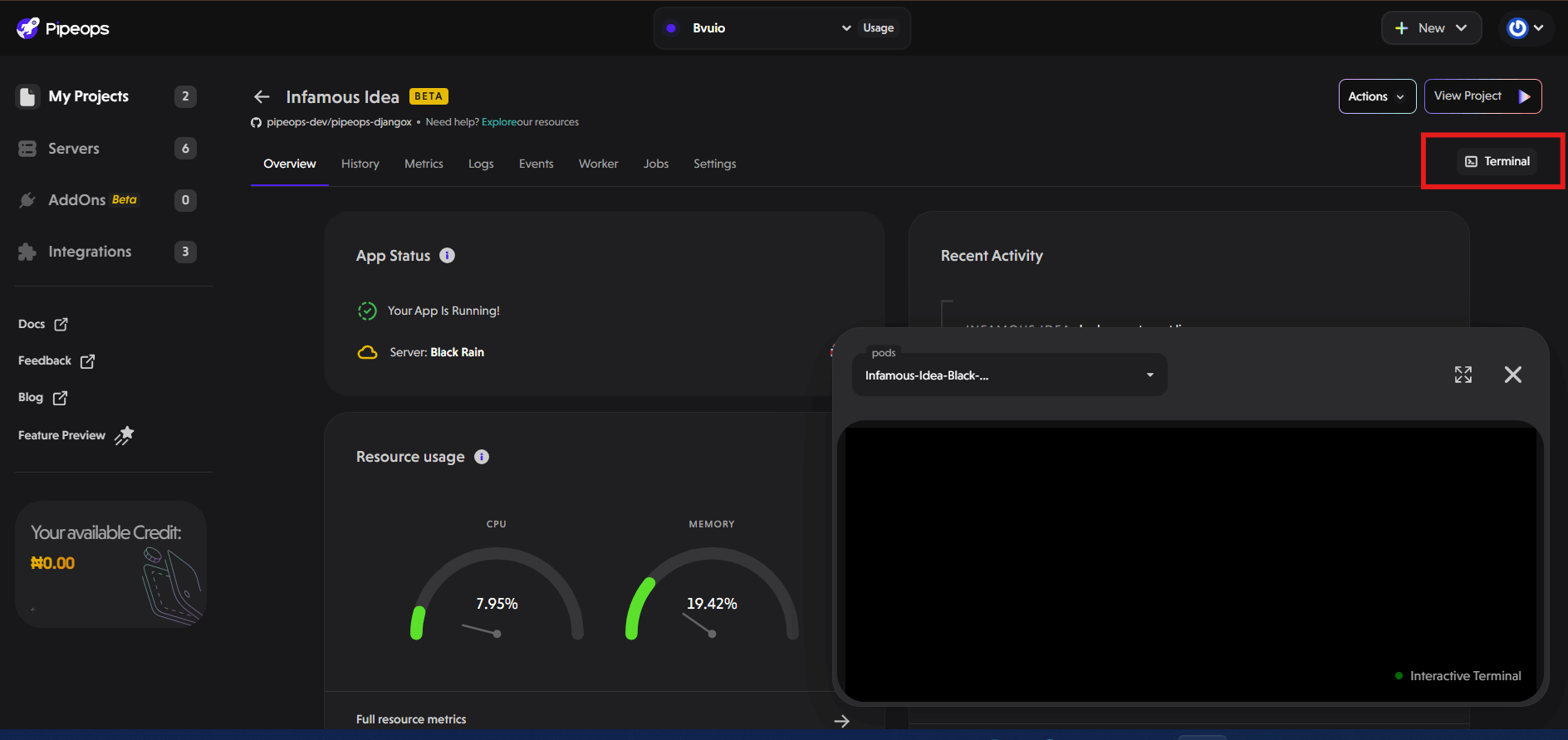
- Navigate to your project's main page in PipeOps.
- Click on the "Terminal" tab at the extreme right side of your screen.
Terminal Pods
The terminal is associated with specific pods within the project's environment, allowing users to execute commands within the context of a particular pod.
Working with Commands
Once inside the terminal, users can run a wide range of commands to manage their project effectively. Some commonly used commands include:
- ls: List directory contents.
- pwd: Print the current working directory.
- df: Display disk space usage.
- du: Estimate file space usage.
Users can execute these commands and more to inspect files, manage directories, monitor resource usage, and perform various administrative tasks within their project's environment.
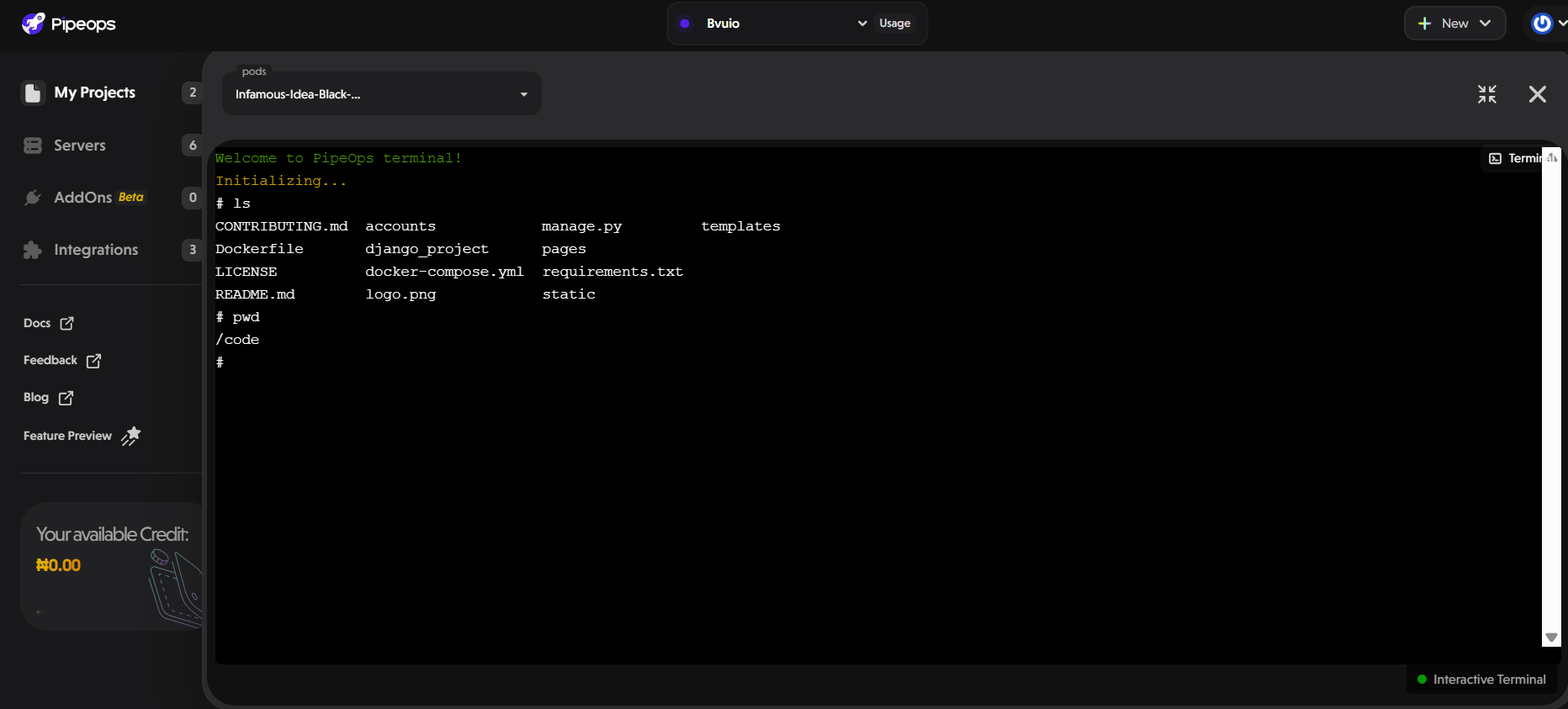
Here's an example of using the terminal in PipeOps to list directory contents (ls) and print the current working directory (pwd)
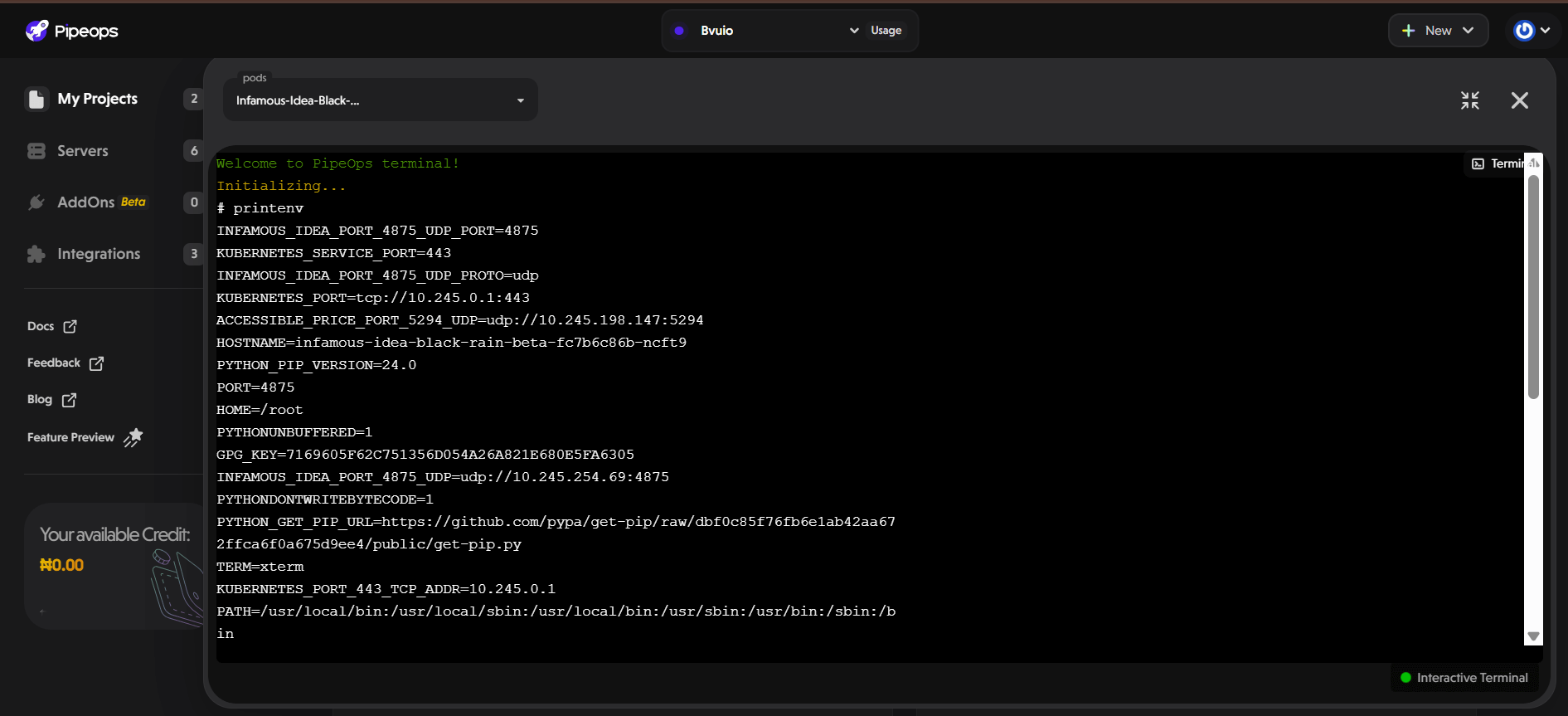
The best part is that the terminal feature includes a convenient selection of commonly used commands, each accompanied by a description of its functionality. This makes it easy for users to find and execute commands, even if they don't remember the exact name. Some of these pre-added commands include PS, FREE, DU, and PRINTENV, providing users with essential tools for managing their projects effectively.
Benefits of the Terminal Feature
- Efficient Resource Management: The terminal provides direct access to project resources, allowing users to manage files, directories, and system processes efficiently.
- Streamlined Workflow: By executing commands directly within the project's environment, users can streamline their workflow and perform tasks without switching between different interfaces or platforms.
- Enhanced Control: With access to the command line interface, users have greater control over their project's environment, enabling them to troubleshoot issues, install dependencies, and customize configurations as needed.
In summary, the terminal feature in PipeOps offers a powerful interface for managing projects, enabling users to execute commands directly within their project's environment and streamline their workflow effectively. Whether inspecting files, monitoring resources, or performing administrative tasks, the terminal provides a versatile and efficient tool for project management.